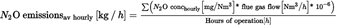- Latest available (Revised)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Commission Regulation (EU) No 601/2012 (repealed)Show full title
Commission Regulation (EU) No 601/2012 of 21 June 2012 on the monitoring and reporting of greenhouse gas emissions pursuant to Directive 2003/87/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (Text with EEA relevance) (repealed)
You are here:
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
Revised version PDFs
- Revised 01/01/20210.44 MB
- Revised 01/01/20190.99 MB
- Revised 30/07/20141.41 MB
- Revised 01/01/20131.41 MB
- Revised 01/08/20121.41 MB
This is a legislation item that originated from the EU
After exit day there will be three versions of this legislation to consult for different purposes. The legislation.gov.uk version is the version that applies in the UK. The EU Version currently on EUR-lex is the version that currently applies in the EU i.e you may need this if you operate a business in the EU.
The web archive version is the official version of this legislation item as it stood on exit day before being published to legislation.gov.uk and any subsequent UK changes and effects applied. The web archive also captured associated case law and other language formats from EUR-Lex.
Changes over time for: Division B.
Changes to legislation:
There are currently no known outstanding effects for the Commission Regulation (EU) No 601/2012 (repealed), Division B..![]()
Changes to Legislation
Revised legislation carried on this site may not be fully up to date. At the current time any known changes or effects made by subsequent legislation have been applied to the text of the legislation you are viewing by the editorial team. Please see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’ for details regarding the timescales for which new effects are identified and recorded on this site.
B. Determination of N2O emissions U.K.
B.1.Annual N2O emissionsU.K.
The operator shall monitor emissions of N2O from nitric acid production using continuous emissions measurement. The operator shall monitor emissions of N2O from adipic acid, caprolactam, glyoxal and glyoxylic acid production using a measurement-based methodology for abated emissions and a calculation-based method (based on a mass balance methodology) for temporary occurrences of unabated emissions.
For each emission source where continuous emissions measurement is applied, the operator shall consider the total annual emissions to be the sum of all hourly emissions using the following formula:
N2O emissionsannual [t] = Σ [N2O conchourly [mg/Nm3] * flue gas flowhourly [Nm3/h]] * 10–9
Where:
=
total annual emissions of N2O from the emission source in tonnes N2O
=
hourly concentrations of N2O in mg/Nm3 in the flue gas flow measured during operation
=
flue gas flow determined in Nm3/h for each hourly concentration
B.2.Hourly N2O emissionsU.K.
The operator shall calculate annual average hourly N2O emissions for each source where continuous emission measurement is applied using the following equation:
Where:
=
annual average hourly N2O emissions in kg/h from the source;
=
hourly concentrations of N2O in mg/Nm3 in the flue gas flow measured during operation;
=
flue gas flow determined in Nm3/h for each hourly concentration.
The operator shall determine hourly N2O concentrations [mg/Nm3] in the flue gas from each emission source using a measurement-based methodology at a representative point, after the NOx/N2O abatement equipment, where abatement is used. The operator shall apply techniques capable of measuring N2O concentrations of all emission sources during both abated and unabated conditions. Where uncertainties increase during such periods, the operator shall take them into account in the uncertainty assessment.
The operator shall adjust all measurements to a dry gas basis where required and report them consistently.
B.3.Determination of flue gas flowU.K.
The operator shall use the methods for monitoring flue gas flow set out in Article 43(5) of this Regulation for measuring the flue gas flow for N2O emissions monitoring. For nitric acid production, the operator shall apply the method in accordance with point (a) of Article 43(5) unless it is technically not feasible. In that case and upon approval by the competent authority, the operator shall apply an alternative method, including by a mass balance methodology based on significant parameters such as ammonia input load, or determination of flow by continuous emissions flow measurement.
The flue gas flow shall be calculated in accordance with the following formula:
Vflue gas flow [Nm3/h] = Vair * (1 – O2,air)/(1 – O2,flue gas)
Where:
=
Total input air flow in Nm3/h at standard conditions;
=
Volume fraction of O2 in dry air [= 0,2095];
=
Volume fraction of O2 in the flue gas.
The Vair shall be calculated as the sum of all air flows entering the nitric acid production unit.
The operator shall apply the following formula, unless stated otherwise in its monitoring plan:
Vair = Vprim + Vsec + Vseal
Where:
=
Primary input air flow in Nm3/h at standard conditions;
=
Secondary input air flow in Nm3/h at standard conditions;
=
Seal input air flow in Nm3/h at standard conditions.
The operator shall determine Vprim by continuous flow measurement before the mixing with ammonia takes place. The operator shall determine Vsec by continuous flow measurement, including where the measurement is before the heat recovery unit. For Vseal the operator shall consider the purged airflow within the nitric acid production process.
For input air streams accounting for cumulatively less than 2,5 % of the total air flow, the competent authority may accept estimation methods for the determination of that air flow rate proposed by the operator based on industry best practices.
The operator shall provide evidence through measurements under normal operating conditions that the flue gas flow measured is sufficiently homogeneous to allow for the proposed measurement method. Where non-homogeneous flow is confirmed through these measurements, the operator shall take that into account when determining appropriate monitoring methods and when calculating the uncertainty in the N2O emissions.
The operator shall adjust all measurements to a dry gas basis and report them consistently.
B.4.Oxygen (O2) concentrationsU.K.
The operator shall measure the oxygen concentrations in the flue gas where necessary for calculating the flue gas flow in accordance with subsection B.3 of this section of Annex IV. In doing so, the operator shall comply with the requirements for concentration measurements within Article 41(1) and (2). In determining the uncertainty of N2O emissions, the operator shall take the uncertainty of O2 concentration measurements into account.
The operator shall adjust all measurements to a dry gas basis where required and report them consistently.
B.5.Calculation of N2O emissionsU.K.
For specific periods of unabated emissions of N2O from adipic acid, caprolactam, glyoxal and glyoxylic acid production, including unabated emissions from venting for safety reasons and when abatement plant fails, and where continuous emissions monitoring of N2O is technically not feasible, the operator shall subject to the approval of the specific methodology by the competent authority calculate N2O emissions using a mass balance methodology. For this purpose the overall uncertainty shall be similar to the result of applying the tier requirements of Article 41(1) and (2). The operator shall base the calculation method on the maximum potential emission rate of N2O from the chemical reaction taking place at the time and the period of the emission.
The operator shall take the uncertainty in any calculated emissions for a specific emission source into account in determining the annual average hourly uncertainty for the emission source.
B.6.Determination of activity production ratesU.K.
Production rates shall be calculated using daily production reports and hours of operation.
B.7.Sampling ratesU.K.
Valid hourly averages or averages for shorter reference periods shall be calculated in accordance with Article 44 for:
concentration of N2O in the flue gas;
total flue gas flow where this is measured directly and where required;
all gas flows and oxygen concentrations necessary to determine the total flue gas flow indirectly.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Regulation
PrintThe Whole Annex
PrintThe Whole Division
PrintThis Division only
You have chosen to open the Whole Regulation
The Whole Regulation you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open Schedules only
The Schedules you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources